sccm: computers with names greater than 15 characters
and coincidentally, blog posts with really long titles.
if you run into scenarios where you find that computers with longer than 15 characters are exhibiting strange issues in an application, you can root out these computers with configmgr or AD. while the computer itself may show a longer than 15 character machine name, the records for it in AD and configmgr show a truncated value.
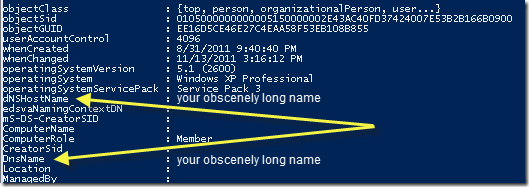
this is interesting because the computer is registered with its long name in DNS. it can "interesting" when you see a truncated name that doesn't resolve (especially where WINS is involved and handles the resolution for netbios lookup adding further confusion.)
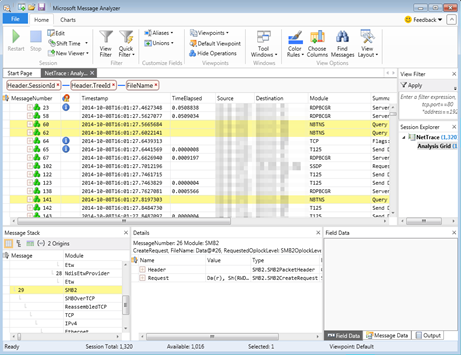
funny enough, where you root out this problem exists kind of on the same plane for both AD and configmgr. it's the DNS host name that gives it away! take a look a these screenshots -- from SCCM and AD, respectively:
(removed the computer names out of this screenshot)
so what do you do with this information, now that you know? well, let's look at ways of identifying it.
first of all, you can count out the characters to see how many are in the name. since dnsname and dnshostname have the same thing, we could use something like this:
((Get-QADComputer myComputer).dnshostname.split(".")[0]) | Measure-object -Character
Characters
----------
16
now we can loop that into a general search for the entire domain:
Get-QADComputer -SearchRoot 'whatev you use' -SizeLimit 0 | where {($_.dnshostname.split(".")[0] | Measure-Object -Character).characters -gt 15}
if sql is your thing and you prefer to query configmgr, here's the sql query:
select distinct dnshostname0
from dbo.v_GS_NETWORK_ADAPTER_CONFIGUR
where LEN(dnshostname0) > 15
hope that helps!

Comments
Post a Comment